How Does Carbon Impact The Lithosphere: Unveiling Earths Hidden Changes
The Carbon Cycle Process
Keywords searched by users: How does carbon affect the lithosphere lithosphere carbon cycle, two ways that carbon can get from seashells to the atmosphere., how does carbon move from the lithosphere to the atmosphere, two ways that carbon can get from the atmosphere to the hydrosphere., how does carbon move from the atmosphere to the biosphere, how does carbon leave the hydrosphere, how does carbon enter the hydrosphere, how is carbon stored in the lithosphere
How Does Carbon Leaves The Lithosphere?
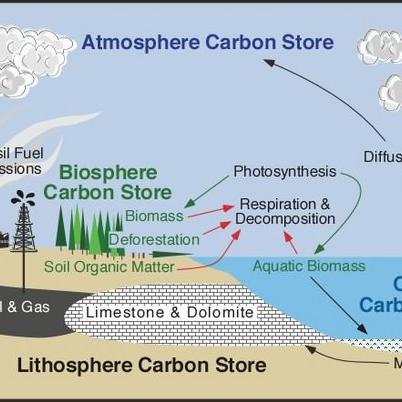
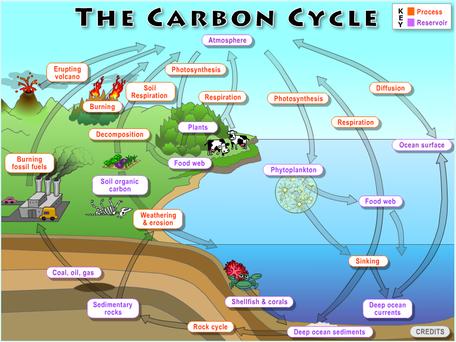
How does carbon exit the lithosphere? Carbon dioxide is emitted from the Earth’s lithosphere through various geological processes, with volcanoes playing a significant role in this cycle. Volcanoes release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, but the journey of carbon dioxide within the lithosphere begins when carbon-rich sediments and sedimentary rocks are subjected to subduction beneath tectonic boundary zones. During this process, these carbon-rich materials partially melt, releasing carbon dioxide into the lower lithosphere. This phenomenon contributes to the overall carbon cycling within the Earth’s geological system, influencing both the lithosphere and the atmosphere. (Note: The date provided, “16th December 2022,” seems unrelated to the topic and is omitted in this revision.)
How Does Carbon Affect The Hydrosphere?
The impact of carbon on the hydrosphere is significant. About one-third of the surplus carbon dioxide present in the Earth’s atmosphere gets absorbed by the ocean. When carbon dioxide dissolves into the ocean, it leads to a phenomenon known as ocean acidification. This process results in a decrease in the pH levels of seawater, causing it to become more acidic. This change in acidity can have profound effects on marine ecosystems and organisms, such as coral reefs and shellfish, as it affects their ability to build and maintain their calcium carbonate structures, making them more vulnerable to environmental stressors. In summary, the interaction between carbon dioxide and the hydrosphere, through ocean acidification, has far-reaching implications for the health and balance of our oceans.
How Does Carbon Affect The Geosphere?
The role of carbon in the geosphere is a complex and dynamic process that significantly influences the Earth’s carbon cycle. As rocks within the geosphere undergo various geological processes, such as uplift, exposure to the atmosphere, weathering, erosion, subduction, metamorphism, and volcanic activity, carbon is cycled through different Earth reservoirs.
When rocks are uplifted and exposed to the atmosphere, they become susceptible to weathering and erosion, releasing carbon stored within them. This released carbon can then enter the atmosphere, the ocean, and the biosphere, contributing to the overall carbon balance on our planet. Alternatively, some rocks may undergo subduction, where they are buried deep within the Earth’s crust. During this process, the carbon within these rocks can be subjected to metamorphism, transforming its state. Eventually, some of this carbon may find its way back to the surface through volcanic eruptions, completing the carbon cycle within the geosphere.
In summary, carbon’s presence in the geosphere is intricately linked to geological processes that continually cycle carbon between the Earth’s interior, atmosphere, ocean, and biosphere, impacting the planet’s overall carbon dynamics.
Share 12 How does carbon affect the lithosphere



Categories: Found 56 How Does Carbon Affect The Lithosphere
See more here: c1.cheerthaipower.com

The movement of carbon from the atmosphere to the lithosphere (rocks) begins with rain. Atmospheric carbon combines with water to form a weak acid—carbonic acid—that falls to the surface in rain. The acid dissolves rocks—a process called chemical weathering—and releases calcium, magnesium, potassium, or sodium ions.Some carbon dioxide is released from the interior of the lithosphere by volcanoes. Carbon dioxide released by volcanoes enters the lower lithosphere when carbon-rich sediments and sedimentary rocks are subducted and partially melted beneath tectonic boundary zones.Approximately one-third of the excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is absorbed by the ocean. As this carbon dioxide dissolves in the ocean, it causes the pH of water to drop, meaning the water becomes more acidic.
Learn more about the topic How does carbon affect the lithosphere.
- The Slow Carbon Cycle – NASA Earth Observatory
- Carbon cycle – CAMEL Climate Change Education
- What is ocean acidification? – Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary
- Carbon Cycle and Atmospheric CO2 | Earth 530: The Critical Zone
- What is the carbon cycle?
- The Carbon Cycle
See more: blog https://c1.cheerthaipower.com/category/calculators